Overview of this book
Embedded Linux runs many of the devices we use every day, from smart TVs to WiFi routers, test equipment to industrial controllers - all of them have Linux at their heart. Linux is a core technology in the implementation of the inter-connected world of the Internet of Things.
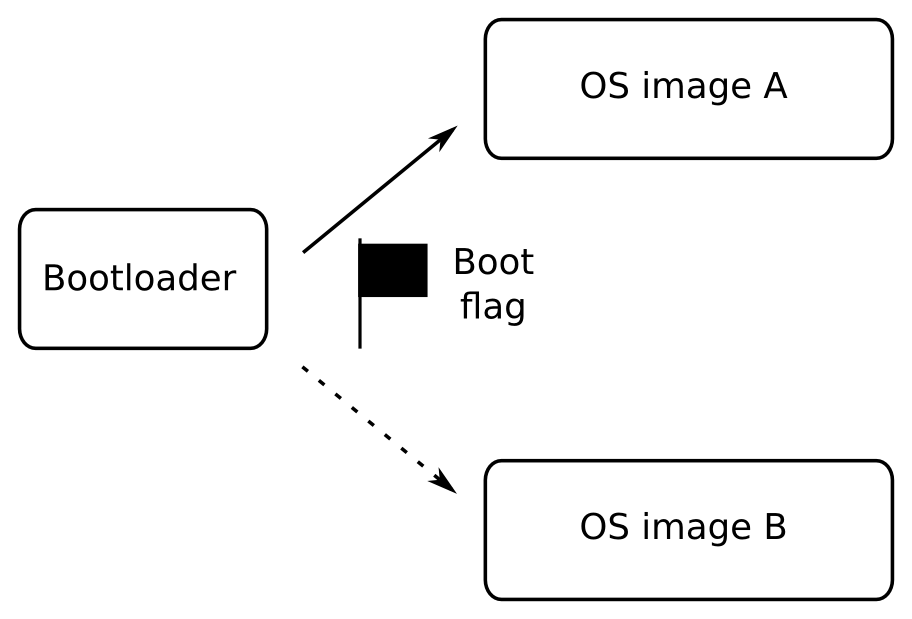
You will begin by learning about the fundamental elements that underpin all embedded Linux projects: the toolchain, the bootloader, the kernel, and the root filesystem. You’ll see how to create each of these elements from scratch, and how to automate the process using Buildroot and the Yocto Project.
Moving on, you’ll find out how to implement an effective storage strategy for flash memory chips, and how to install updates to the device remotely once it is deployed. You’ll also get to know the key aspects of writing code for embedded Linux, such as how to access hardware from applications, the implications of writing multi-threaded code, and techniques to manage memory in an efficient way. The final chapters show you how to debug your code, both in applications and in the Linux kernel, and how to profile the system so that you can look out for performance bottlenecks.
By the end of the book, you will have a complete overview of the steps required to create a successful embedded Linux system.



 Free Chapter
Free Chapter